Table of Contents
Introduction: BIM Empowered Notre-Dame
In many cultures, fire holds a profound symbolic presence as a force of both destruction and renewal. It serves as a sacred element in rituals, embodying rebirth, transformation, and knowledge. For instance, in Greek mythology, Prometheus’ act of stealing fire from the gods symbolizes humanity’s progress, creativity, and enlightenment.
However, fire’s dual nature is equally evident in its capacity for destruction, as portrayed in the biblical tale of Sodom and Gomorrah, where it acted as an instrument of divine punishment.

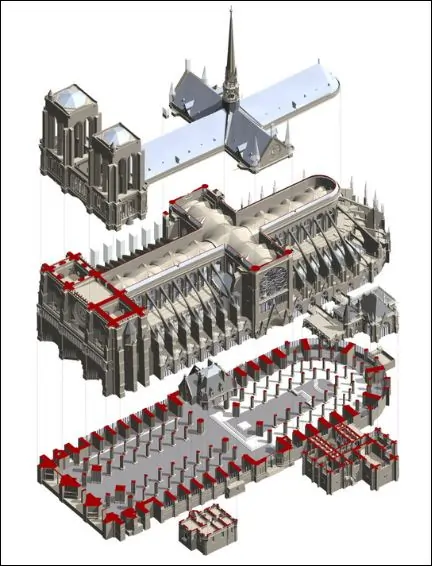
“We collected billions of points to capture every intricate detail of the cathedral, from its vaulted ceilings to its iconic spire. Because of the complex structural details and sheer size of the Notre-Dame, it took over a year to create the full-scale model as it existed before the fire. No one had built a spire like this in over 100 years, and the 3D model was used to guide the new design to honor its historic integrity as well as test and understand its stability against storms.” – Nicolas Mangon
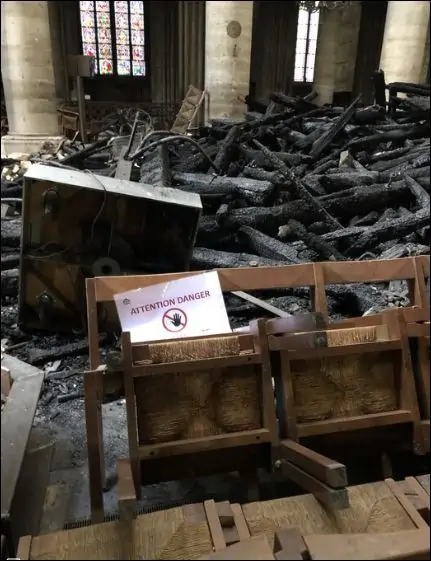
This duality of fire was strikingly demonstrated during the 2019 Notre-Dame Cathedral fire. The catastrophic event devastated the iconic structure but also ignited a global wave of solidarity and an unprecedented effort to restore one of Western civilization’s most treasured landmarks.
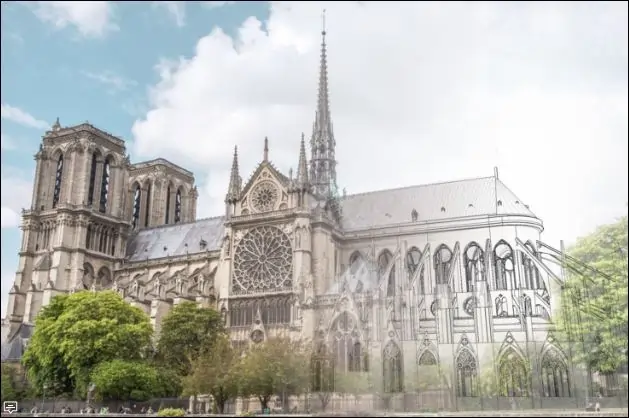

“The 3D BIM model was the solution to these challenges; it enhanced collaboration, clarity, and efficiency across the reconstruction teams, was used to simulate and plan every phase of construction, and predicted issues that could arise before they occurred on the jobsite. The BIM model, and our software, which Autodesk donated to the Établissement public Rebâtir Notre-Dame de Paris, provided a shared and scalable 3D database to guide collaboration amongst the project’s architects, engineers, and historians”. – Nicolas Mangon
The Immediate Response to Notre-Dame’s Tragedy
Even before the flames were fully extinguished, the world came together to support the restoration of Notre-Dame. Donations poured in, totaling over $1 billion. This collective effort underscored the cathedral’s significance as a cultural and historical symbol, not just for France but for humanity at large.

Among the key contributors to the restoration was Autodesk, a leader in design software and technology. The company provided cutting-edge tools and expertise, creating a detailed Building Information Modeling (BIM) model of the cathedral.
This digital reconstruction played a critical role in addressing the challenges of restoring a monument with limited original documentation.
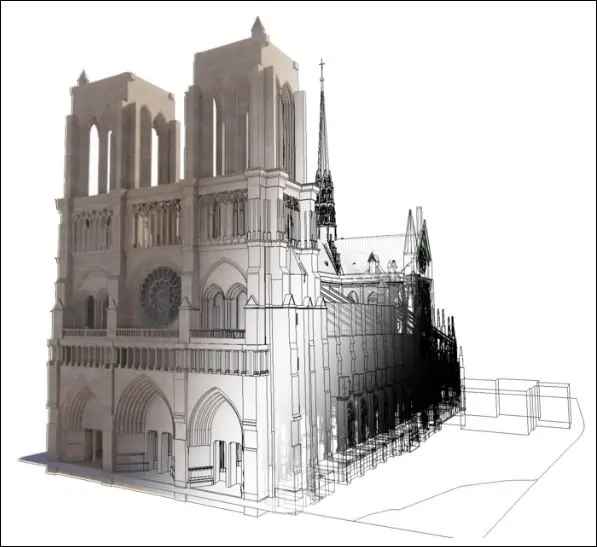

How BIM Empowered Notre-Dame’s Restoration
1. The Creation of a Digital Twin
The restoration process began with the creation of a highly accurate 3D BIM model. This was achieved through:
- Laser Scanning: Capturing intricate architectural details.
- Photogrammetry: Converting photographs into precise measurements.
- Drone Footage: Documenting hard-to-reach areas.
The resulting digital twin mirrored the cathedral’s pre-fire state, preserving its historical authenticity.
2. Collaboration Among Experts
The project brought together over 200 companies and 2,000 individuals, including architects, engineers, and historians. The shared BIM platform acted as a central repository for all data, facilitating seamless collaboration.
3. Addressing Restoration Challenges
Three major challenges were tackled using BIM technology:
- Tight Timeline: The goal was to complete restoration within five years.
- Limited Documentation: BIM compensated for gaps in historical records.
- Complex Logistics: Simulating worker routes, material deliveries, and construction phases enhanced efficiency and safety.
4. Ensuring Historical and Structural Integrity
BIM enabled precise planning and simulation of the construction phases, identifying potential issues early. Modern engineering principles were integrated to enhance the structure’s resilience against environmental stressors like storms, ensuring both safety and historical fidelity.
Broader Implications of BIM Empowered Notre-Dame by their Technology
The success of Notre-Dame’s restoration highlights BIM’s transformative potential in preserving cultural heritage. Beyond restoration, BIM’s predictive capabilities allow for:
- Simulating Environmental Impacts: Anticipating how historic structures will respond to climate change.
- Proactive Preservation: Creating digital archives of landmarks to guide future conservation efforts.
This project sets a precedent for using digital tools to protect global heritage sites, ensuring their survival for future generations.
Conclusion
The 2019 Notre-Dame fire was a tragic event, but it also demonstrated humanity’s resilience and ingenuity. The integration of BIM technology not only enabled the cathedral’s restoration but also set new standards for cultural preservation.
This achievement underscores the importance of investing in digital documentation and collaborative technologies to safeguard our shared heritage against the tests of time and unforeseen disasters. Notre-Dame’s restoration is not merely about rebuilding a monument; it’s about preserving history, culture, and identity for centuries to come.
FAQs
1. What is BIM?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital tool that creates precise 3D models of structures, enabling better planning, collaboration, and management in construction and restoration projects.
2. How long did it take to create BIM Empowered Notre-Dame model?
The digital twin of Notre-Dame was created over the course of a year using advanced technologies like laser scanning and drone footage.
3. Why is BIM Empowered Notre-Dame restoration significant?
The project not only restores a cultural landmark but also showcases the potential of modern technology in preserving historical integrity.
Disclaimer
This article: How BIM Empowered Notre-Dame’s Rise from the Ashes is for informational purposes only. While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, the information provided should not be considered exhaustive or a substitute for professional advice in restoration or architectural preservation.
TechWirings does not endorse or explicitly support any views or actions expressed in this content.










